Single Crystal Blade Laser Repair


Single Crystal Blade Laser Repair
The key process parameters for controlling single crystal or directional crystallization are the control of the cooling rate and temperature gradient of the melt pool, where the cooling rate determines the shape of the melt pool and the temperature gradient determines the direction of crystallization growth during solidification of the melt pool. Both of these process parameters can be captured and measured in real time by means of melt pool monitoring and image processing.
Project background
With the continuous improvement of the aerospace industry for the aero-engine performance and thrust-to-weight ratio requirements, the working temperature of the aero-engine hot-end components has further increased, and the performance requirements of the alloy have become higher and higher. nickel-based high-temperature alloys have gradually developed to single crystal with better high-temperature performance, such as Rene N5, CMSX-4, DD432, etc.
And have now developed to the fifth generation of nickel-based single-crystal high-temperature alloys, with each generation of high-temperature alloys having a Along with the material development comes the challenge of manufacturing process, how to use direct metal deposition technology to realize the repair and direct forming of single crystal parts is gradually becoming a research hotspot, and how to ensure its single crystal properties and avoid the generation of stray crystals in the process of repair and forming is the biggest challenge. This requirement can be achieved by using laser cladding technology.
Project sample
It was shown that electron microscopy EBSD scans of cross-sections of single-layer fusion-coated single-crystal alloy materials reveal that directional crystalline organization that continues the epitaxial growth of the substrate crystals can be formed in most areas of the lower part of the fusion-coated layer (blue area in the figure below, the color represents the direction of crystalline growth);
Heterogeneous crystalline organization with different orientations can be formed on the upper surface of the molten cladding layer (colored areas);
From the above observations, it can be concluded that in multilayer cladding, the cladding layer needs to have sufficient melting depth to remelt the heterocrystalline area of the next layer to form a continuously growing single crystal or oriented crystalline organization.
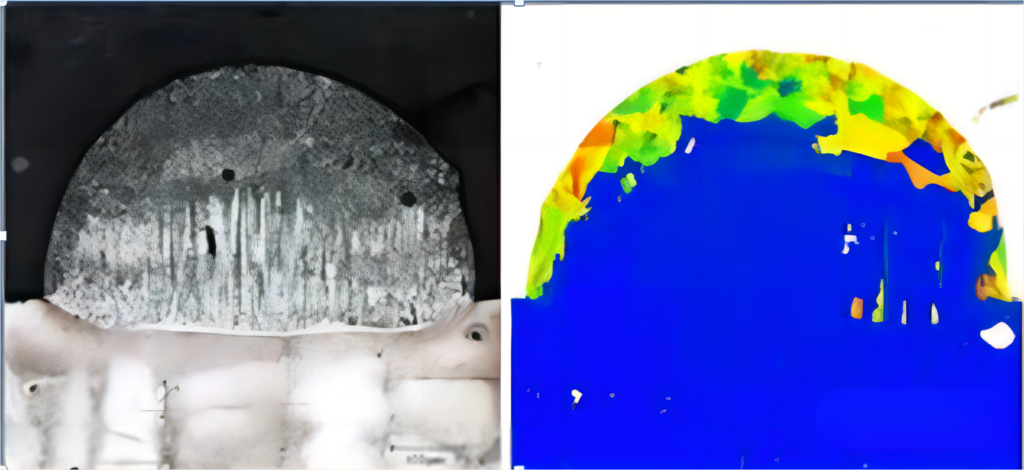


The cladding layer cross-section
Laser melting single crystal material technology results
The key process parameters for controlling single crystal or directional crystallization are the control of the cooling rate and temperature gradient of the melt pool, where the cooling rate determines the shape of the melt pool and the temperature gradient determines the direction of crystallization growth during solidification of the melt pool. Both of these process parameters can be captured and measured in real time by means of melt pool monitoring and image processing.Through the cladding test of the single element, the feasibility of the cladding, the stability of the process, the cladding effect of the single element blade, including deformation, and the presence or absence of defects were confirmed, and the machining allowance and deformation were confirmed through the repair after cladding and so on.
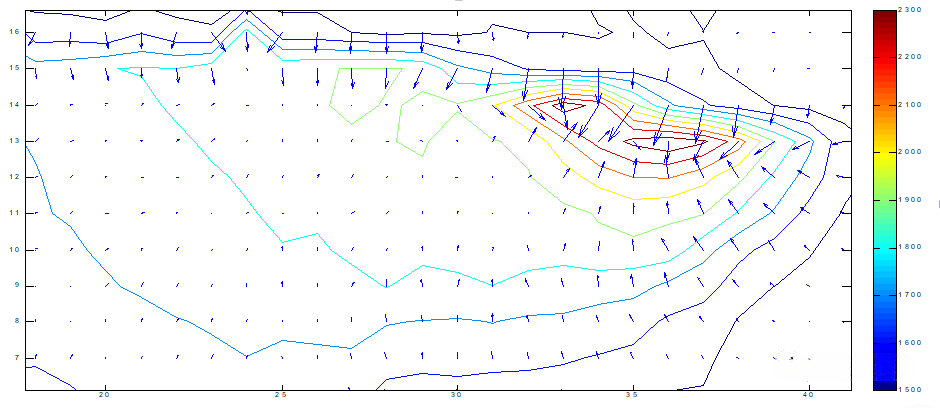

The melt pool temperature gradient figure
Using nickel-based powder material, experiments were conducted on DD432 with good results, and process development tests were conducted on single crystal blades of DD432. The thickness of each part of the single crystal blade tip has a certain difference, the thicker, the more difficult the directional epitaxial joint length, mainly for the melting layer single channel thickness, the more stringent the process requirements, the smaller the process window range. After process optimization research, the following results of laser melting of single crystal materials were achieved:
1. achieving a maximum single-pass melting width of 1.8 mm and continuous stacking up to 10 mm in height;
2. adjustable range of single layer thickness from 0.15 to 0.5 mm;
3、The amount of heterogeneous crystals on both sides is less than 10%;
4、The high temperature tensile property of the bonding interface at 800℃ reaches 91% of the base material, and the strength of the molten layer is not less than 91% of the base material.

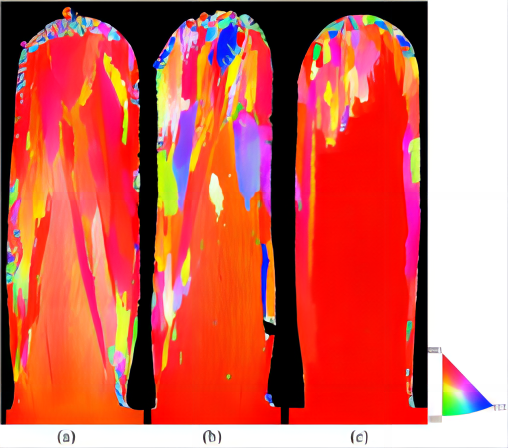
DD432 epitaxial take a long bonding interface


DD432 epitaxial splice length Rene142 cross section full view
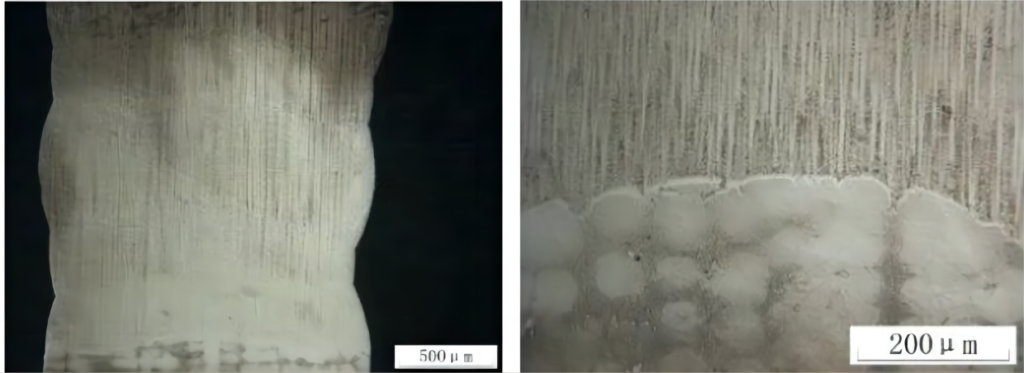
>>Single Crystal Blade fuse cover case
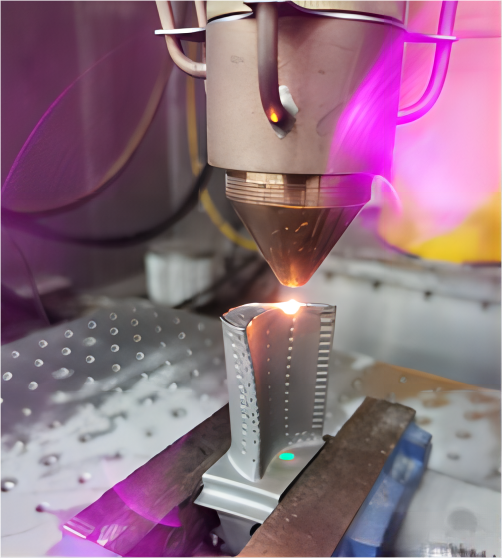


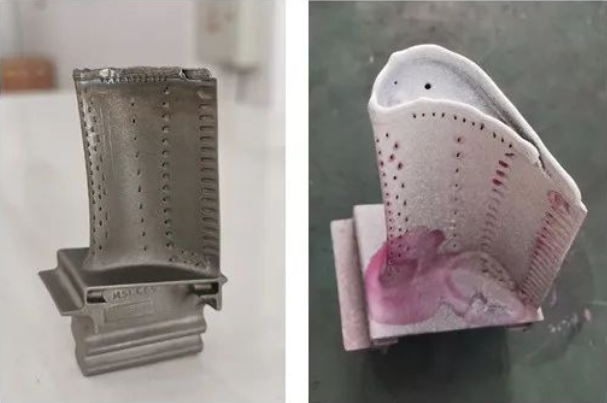

The appearance of the molten cladding layer is smooth and dense, without defects such as cracks and holes visible to the naked eye. Since the melting and cladding process uses two different processes, a more obvious junction area is formed at the junction of different processes of melting and cladding.
