What is laser Cladding?
A stream of metallic powder or wire is fed into a melt pool created by a laser beam as it scans across the target surface, producing a coating of the chosen material.
- Additive manufacturing process using laser technology,CAD/CAM and powder metallurgy.
- Laser Metal Deposition
- Direct Metal laser sintering
- Laser engineered net shaping
- Laser heat source deposits a thin layer of metal on a substrate.
- Melt and add material to an existing part.
Read More:Laser Cladding Unlimited Guide In 2023
laser Cladding Process
- The laser beam is directed at the substrate.
- The substrate absorbs his energy.
- The energy then creates a melt pool.
- In the melt pool, the melted powder particles are combined.
- The fluid flow is caused by the melted pool.
- Solidification occurs quickly.
What is Laser Melting?
Laser metal is an additive manufacturing technology in which metal is heated by a laser and deposited layer by layer onto a metallic substrate. Although technically, laser cladding is a form of laser metal deposition, it is also known as laser cladding. Laser metal deposition is used to create, reinforce, and repair items like turbine blades, pump shafts, and pressure vessels, to mention a few.
- Laser technology, CAD/CAM, and powder metallurgy are used in the additive manufacturing process.
- Layer-by-layer construction of 3D metal parts using metal powder.
- The CAD is divided into layers that specify the two-dimensional portion.
Laser Melting Process
- Slicing the 3D CAD into layers.
- Projection of 2D image in each layer.
- Thin layer of metal powder are distributed onto the substrate.
- Each 2D slice is fused by the laser energy
- Full melting of the particles.
- Is all repeated layer after layer till part is complete.
Laser Melting Application
- Medical applications
- Tooling
- Lightweight construction
- Jewelry
- Tool inserts
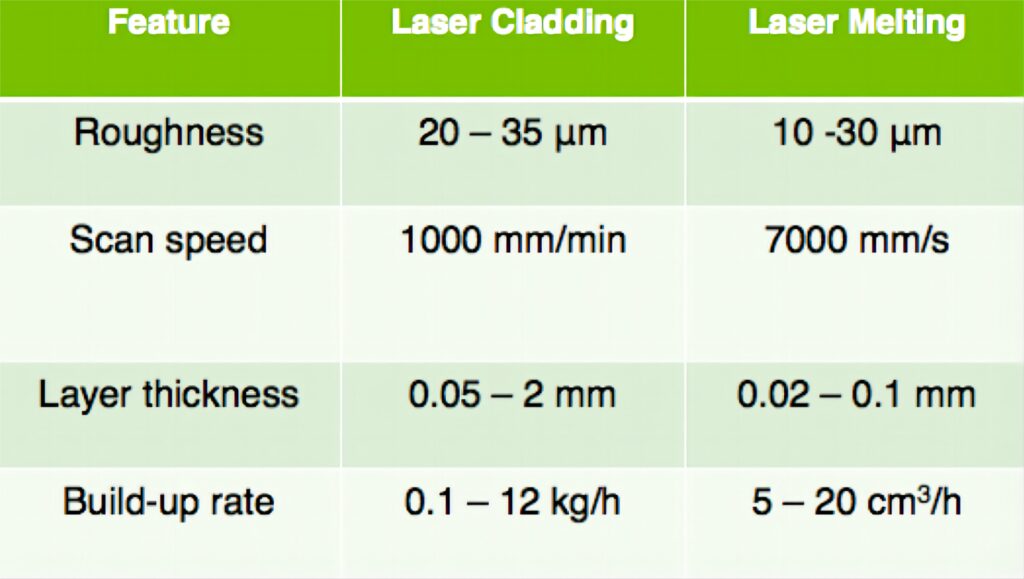
what different between Laser Cladding Vs Laser Melting